Technical File
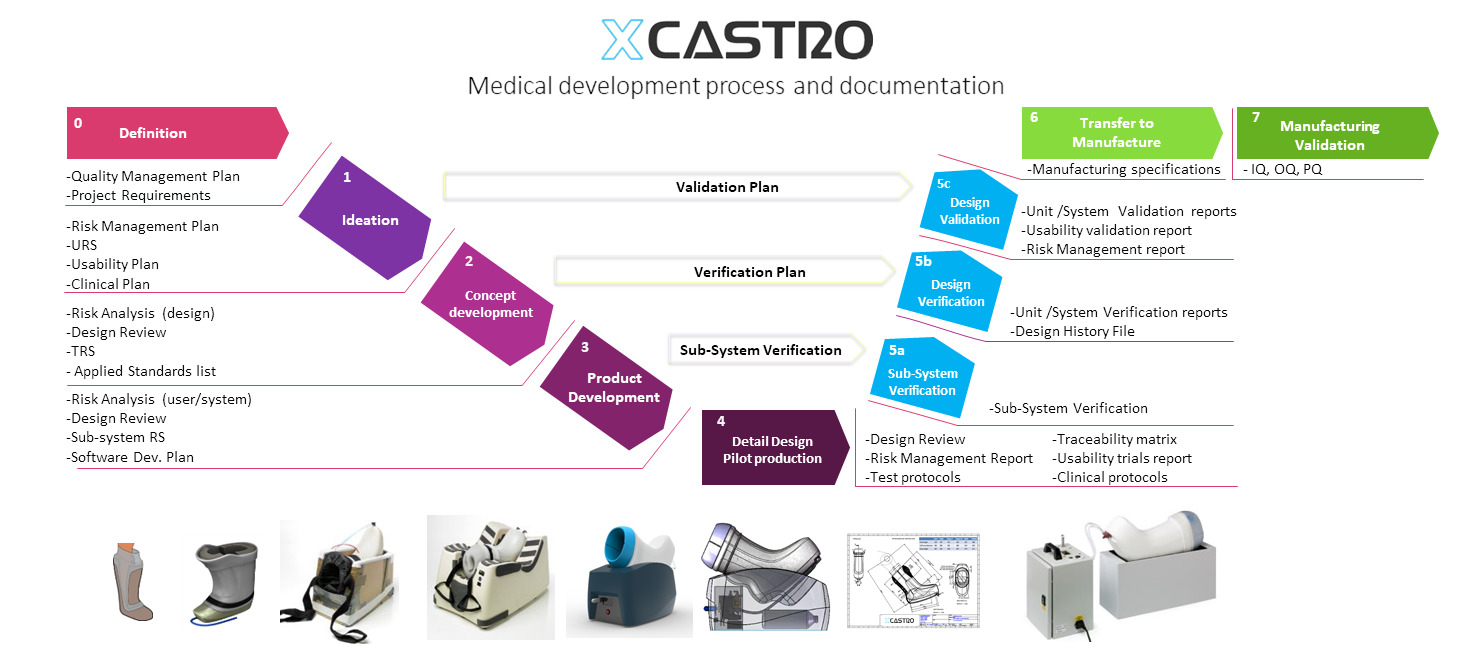
CE and other international regulatory bodies require manufactures to keep a technical file for the product they wish to sell or export. For medical products the requirements for the technical file are stricter and for the FDA it has to include a history file.
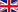
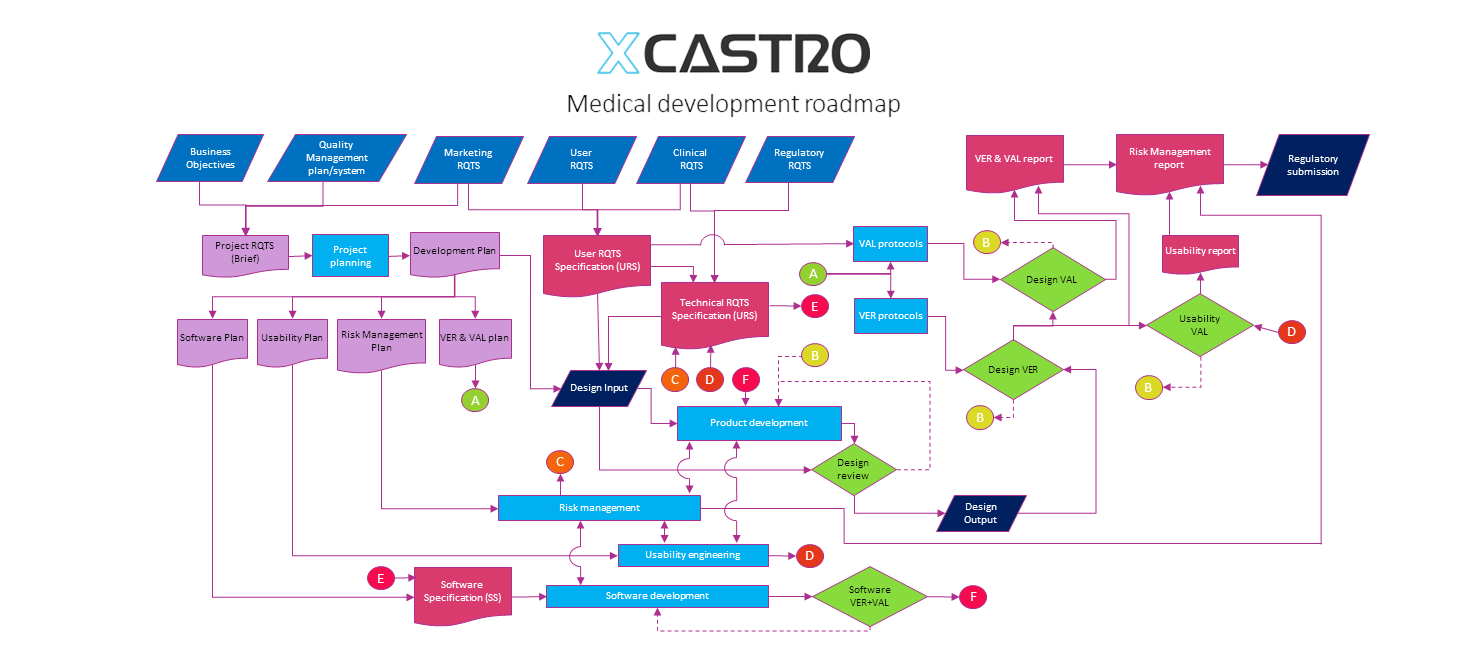
As part of the development activities that I oversee, I look at the compilation of the Technical file and Design History file. In my experience, is always best to work on the technical file documentation as the product evolves, rather than living it at the end. Also, it may require re design in case the requirements and risk management activities are not conducted and documented properly in the early stages.
My design process maps the creation of the required documentation at each stage, so that compilation of a technical file becomes a smooth process. My approach looks how the documentation feeds into the design process and back into the verification activities with a close link during all stages to risk management activities.
These are the usual heading that a technical file would include:
I - Device Description including Variants (Configurations) and Accessories
- Device Description
- Reference to the Manufacturer’s Previous Device Generation(s) and/or Similar Devices or Device History
II - Essential Principles (EP) Checklist
III -Risk Analysis and Control Summary
IV -Design and Manufacturing Information
- Device Design
- Manufacturing Processes
- Manufacturing Sites
V -Product Verification and Validation
- Analytical Performance
- Specimen type
- Analytical performance characteristics
- Clinical Performance
- Stability
- Software Verification and Validation
V- Labelling
Risk Management
For medical products I follow ISO 14971 (Risk management for medical devices). The process is divided in 6 steps that should be conducted and documented properly to comply with the standard
1) Risk Analysis
2) Risk Evaluation
3) Risk Control
4) Residual Risk evaluation
5) Risk Management report
6) Production information
The purpose of Risk management is to demonstrate that the product is safe. If risk management activities are conducted from early stages, then implementing controls becomes a simple task. However, if this is left till the last stages the consequences could have costly implications.
The main tool that is used to analyse and evaluate risk is the FMEA (Failure modes and effect analysis). This tool allow us to lay out the risks and understand the effects that will have and find potential mitigation actions to control them.
FMEA – Failure modes and effects analysis
As part of my development process I use different types of FMEAs to uncover potential product risks. The level of complexity and focus of each FMEA varies depending on the product development stage.
This list highlight the core FMEAs that I usually conduct.
- Concept FMEA – Evaluate ideas
- System FMEA – High level functions
- Design FMEA – Components and features
- Usability FMEA – User interaction
- Software FMEA - Algorithms
- Process FMEA – Manufacturing